THI & UCLA Discovering New Wireless Power Systems For Novel Cardiac Pacing
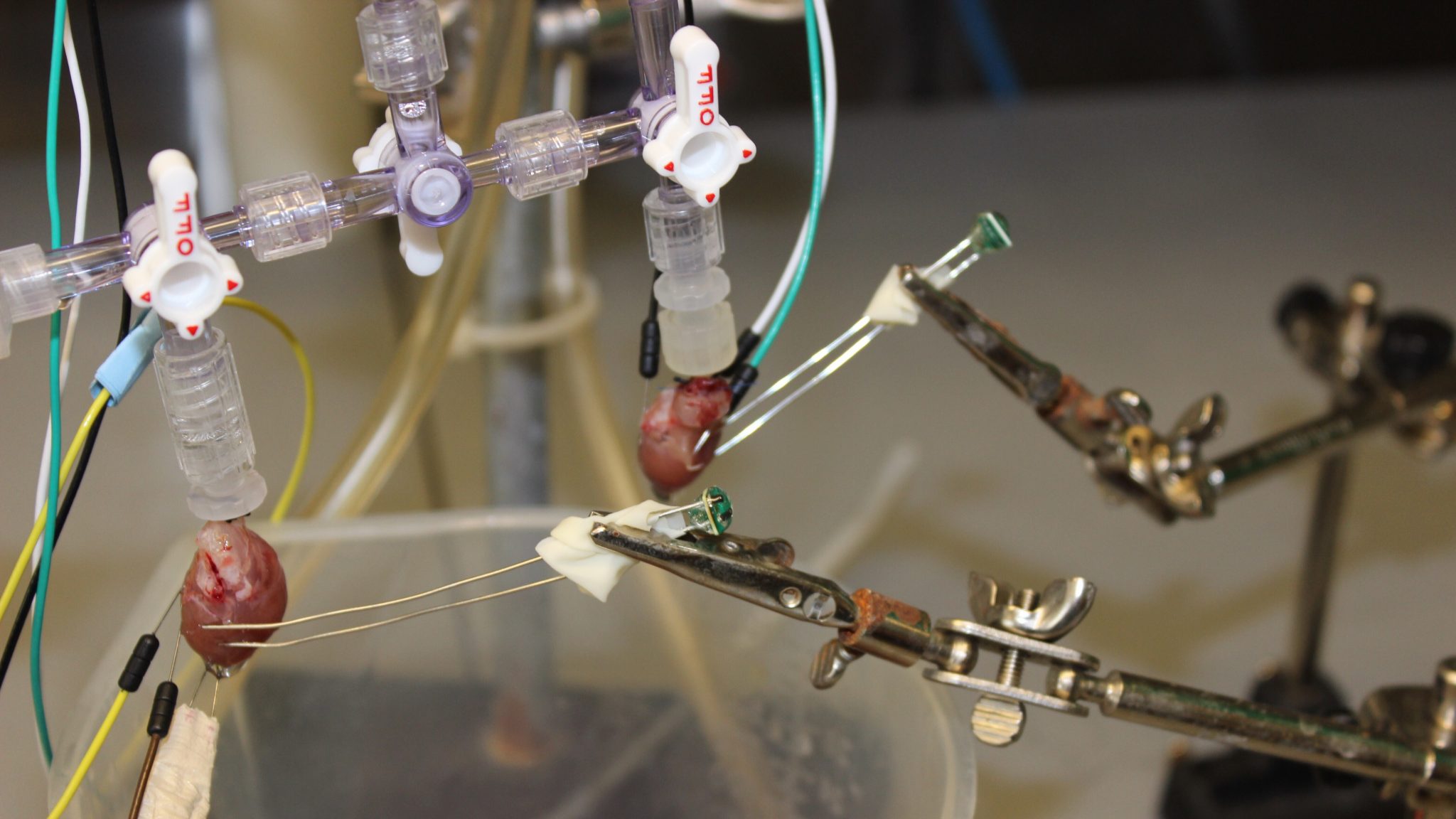
Researchers at THI’s Electrophysiology Clinical Research and Innovations Department in partnership with the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) have discovered a way to use a wireless system to power stimulators to pace multiple sites of the heart.
The work was conducted by THI and UCLA investigators and engineers and scientists in the Regenerative Medicine and Cardiovascular Surgery Research Laboratories at THI and published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology this week.
“This is the first system that offers a new paradigm for programming multi-site pacing devices using miniaturized, wireless, battery-less systems.” According to Dr. Mehdi Razavi, Director of THI’s Electrophysiology Clinical Research and Innovations department.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is used to treat heart failure by synchronously pacing the left and right ventricles and has been shown to provide significant improvement in patients with impaired cardiac systolic function and ventricular dyssynchrony in which there are abnormalities of the ventricles.
Although CRT has shown to improve overall cardiac function, non-responder rates remain as high as 35%. Conventional pacemakers used to deliver CRT are prone to developing a swathe of lead-related complications. Leadless pacemakers provide a feasible alternative to cardiac pacing without the limitations of transvenous leads. Furthermore, leadless pacing using a distributed network of miniaturized pacing sites powered through electromagnetic induction offer the possibility of implantation of numerous pacing sites with an economy of space.
The new study highlights the potential and demonstrates the feasibility of overcoming the limitations of current leadless pacemaker design and is the first to demonstrate the ability to power multiple pacing nodes.
This work was conducted by the collaborative team of researchers led by Mehdi Razavi, MD and Aydin Babakhani, PhD including: Hongming Lyu, Mathews John, David Burkland, Brian Greet, Yutao Xi, Luiz Sampaio, and Doris A. Taylor.
The findings offer support and a conceptual framework for future iterations and eventual clinical utility of wireless power transfer technologies for multisite cardiac pacing— including the wireless and leadless pacemaker system in development at THI.
Read the full article published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology
Lyu H, John M, Burkland D, et al. Leadless multisite pacing: A feasibility study using wireless power transfer based on Langendorff rodent heart models. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2018;29:1588-1593. doi.org/10.1111/jce.13738
Special thank you to Payton Campbell for her assistance with this news story.
About Texas Heart Institute
The Texas Heart Institute (THI), founded by world-renowned cardiovascular surgeon Dr. Denton A. Cooley in 1962, is a nonprofit organization dedicated to reducing the devastating toll of cardiovascular disease through innovative and progressive programs in research, education and improved patient care. More information about THI (@Texas_Heart) is available at www.texasheart.org.

.svg)


